Guest post by Lena Karamanidou, Bernd Kasparek and Simon Campbell. Lena Karamanidou is a researcher at the Department of Economics and Law, Glasgow Caledonian University. Her recent work has focused on the EU border agency Frontex, pushbacks and border violence at the Greek-Turkish land border. Simon Campbell is a field coordinator with the Border Violence Monitoring Network, a collective of organisations and initiatives based in South Eastern Europe documenting pushbacks and violence within state borders. Bernd Kasparek is an undisciplined cultural anthropologist, with a focus on migration and border studies, europeanisation, racism and (digital) infrastructures. His book "Europa als Grenze" (Europe as Border), an ethnography of the European border agency Frontex is forthcoming in Summer 2021.


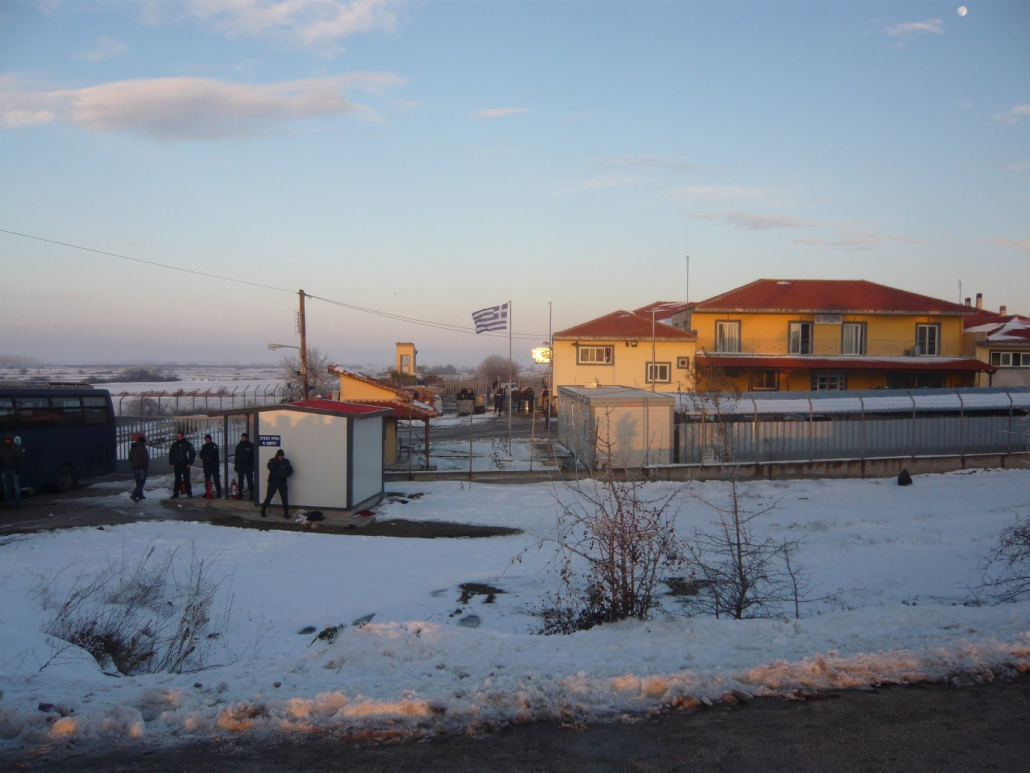
The local coach from Alexandroupoli to Orestiada, the two largest towns in Evros, the region of the Greek-Turkish border, passes outside two border guard stations: Tychero and Neo Cheimonio [images 1 & 2]. Their function as detention spaces is barely discernible from the road; without the Hellenic police signs and vehicles outside, the Tychero border guard station could be mistaken for the wheat warehouse it once was. The train between the two cities, though, passes behind the Tychero facility; from there you can see a gated structure at the back of the station, resembling prison railings, which may have been used as a kind of ‘outside space’ for detainees. Reports by the Committee for the Prevention of Torture (CPT) and the Greek Council for Refugees criticised the absence of outside space and conditions of detention (described sarcastically as ‘best of the best’ by a police officer interviewed by one of the authors in 2011).

Although the Greek government announced the closure of the Tychero station in 2013, after several critical reports on conditions of detention there, it continued to be used as a detention space. While detention facilities may be perceived as stable, permanent or at least long-term structures at the core of European border regimes, their histories in Evros suggest temporal, spatial and functional disruptions. The creation of detention facilities since the 1990s appeared to be ad hoc, reflecting the increasing significance of the area as a key entry point to the European Union and the Europeanisation of border management both nationally and locally.

Spaces for detention were created out of existing facilities such as cells in local police stations and in border guard stations. The latter were established in 1999 - some of which are housed together with police stations, like in the towns of Feres [image 3] and Soufli, and others in separate facilities as in the villages of Tychero, Isaakio and Neo Cheimonio. While it is difficult to find specific information on their history, some detention facilities emerged early in the 2000s, for example in the village of Venna in the Rhodopi prefecture near the boundary with Evros. The Fylakio facility [image 4] was established as a detention centre in 2007 before being renamed a pre-removal centre following legal reforms in 2012. Yet, detention capacity in the area never quite met the needs imposed by the extensive use of detention as an instrument of control. Until the early 2010s, ad hoc, makeshift structures and centres were used at different times in Feres and at the villages of Dikaia, Vrissika [image 5], Elafochori [image 6] and Peplos – all now closed, as well as the one in Venna. The Venna, Peplos, Vrissika, Elafochori and Tychero facilities, as well as the temporary Feres structure referred to in the 1999 CPT report, were all repurposed wheat warehouses, formerly property of a state agricultural agency closed down in the early 1990s.


The facilities mentioned above are official ones. Their function can be traced in official documents – Greek, European and international - as well as in reports by NGOs and human rights organisations and research. However, they are not the only spaces where people may be detained in the area. One example of a ‘quasi-official’ place is the detention facility in Poros [image 7]. Originally a military structure that was converted into a ‘reception’ facility where screening, identification and debriefing procedures took place in 2012, by the late 2010s the centre had fallen into obscurity. From 2015 until 2020, there was little evidence of its use other than a few administrative documents and media reports, and it is unclear when its function switched from a reception to a detention facility. It was only in 2020, through research, investigations and journalism that the Poros facility became ‘known’ again, coinciding with the border spectacle in Evros that year. The government denied that the facility was ‘secret’ – ‘if the New York Times know about it, then I don’t see how such a detention centre can be a secret’, stated the government spokesman. Yet, the CPT described the facility as ‘semi-official’ and supported claims that it was used as a holding facility prior to pushbacks, given ‘the complete absence of any registration of detention’.
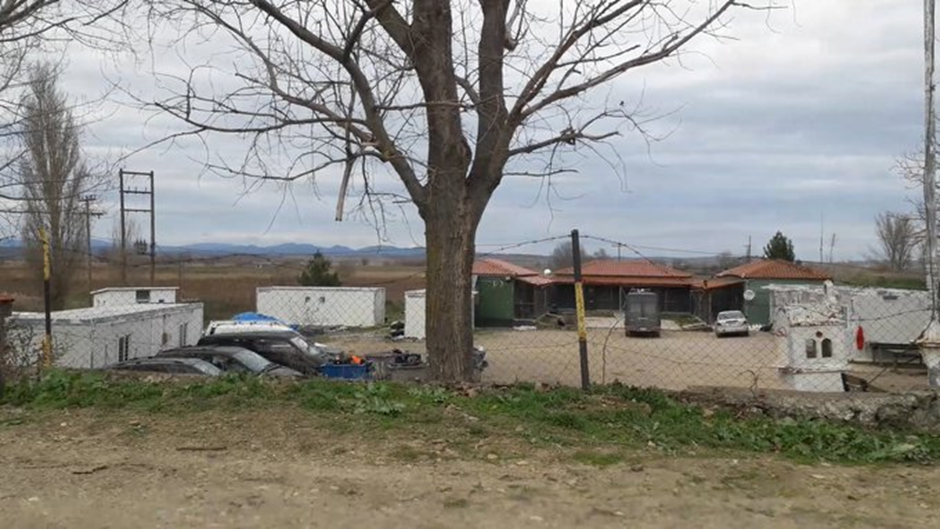

To date, Poros is probably the only facility whose use as a ‘hidden’ detention centre was revealed . Testimonial evidence collected by NGOs and research organisations (for example here, here and here) suggests that detention in informal facilities prior to pushbacks may be a common practice in the area. These sites are used to hold groups captured within the footfall area of the border, but also to receive detainees transferred from across the Greek interior, from urban areas, police stations, and pre-removal detention facilities. Their aggregate role in pooling people-on-the-move prior to pushbacks to Turkey is also intimated by their bare functional layout [image 8]. Several testimonies of people who have been pushed back from Evros to Turkey refer to detention in buildings that did not appear to be police or border guard stations, and were not properly equipped with toilets, running water or beds. The holding cells recounted in these testimonies were composed of fenced yards, portacabins, warehouses, garages, and even animal pens:
“the room did not look like a normal prison or police station but more like a stable”
“They drove us to an old room close to the river. It was a stable. It didn’t have a proper floor, but dirt”.
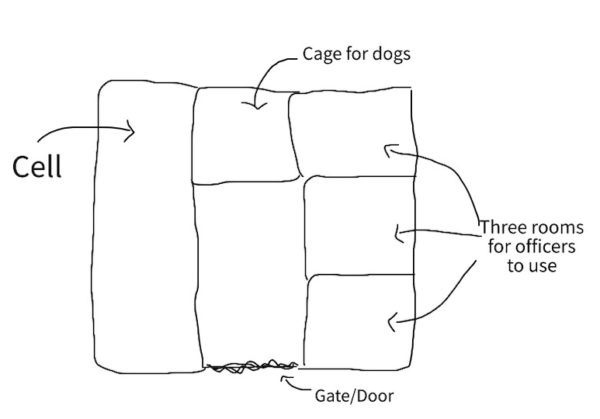
Illustration of a detention site in Evros, as described in a report taken by Josoor (member of the Border Violence Monitoring Network) 2021
https://www.borderviolence.eu/violence-reports/april-8-2021-0600-island-near-karayusuflu/
This unofficial repurposing of agrarian or semi-industrial outbuildings for detention in some senses mirrors the improvised architecture Greek authorities used to expand its official sites in Evros from the 90s onwards. Yet without the formal authorisation, nor the visual signifiers demarcating these sites, the web of new – and possibly old - unofficial detention centres are extremely difficult to locate. People detained there often do not know the exact location because of the way they are transported. Speaking to people who had likely been detained in Tychero, testimonies published by the Border Violence Monitoring Network described how “since the vehicle had no windows, the respondent could not see the building from the outside.” For researchers and investigators, geolocating these sites has become a near impossible task, not only because of the secrecy that characterises the practices of pushbacks and the risks of in situ research, but also because of multiple potential locations and a large number of buildings that could serve as informal detention facilities.
Detention in Greece has been a core technique for governing migration, reflecting policies of illegalisation and criminalising unauthorised entry, even if deportations, which provided one of the key reasons for detention, were not feasible. However, the linkages between detention and pushbacks at the Greek – Turkish border illustrate how the governance of borders relies on assemblages of both formal and informal practices and infrastructures. The proliferation of these structures, often concealed by their benign outward appearance as farm buildings, fits in with the dispersed geography of pushbacks - and the way detention is increasingly serving as a temporal stage within the execution of violent removals.
Any comments about this post? Get in touch with us! Send us an email, or post a comment here or on Facebook. You can also tweet us.
__________
How to cite this blog post (Harvard style)
Karamanidou, L, Kasparek, B. and Campbell, S. (2021). Spaces of Detention at the Greek-Turkish Land Border. Available at: https://www.law.ox.ac.uk/research-subject-groups/centre-criminology/centreborder-criminologies/blog/2021/05/spaces-detention [date]
Share:








